¶ Purpose
The Bank Details screen allows the user to maintain master data such as bank names, account numbers and cheque details of the company (internal). These details are required for processing payments and receipts.
¶ Prerequisites
- Access rights must be assigned to the responsible user for the Bank Details.
¶ Add Bank Details
The Bank Details screen allows the user to add new bank details and edit existing bank details.
Navigation: Main – Menu ➔ Transactions ➔ Finance ➔ Finance Entries ➔ Finance ➔ Financial Year Selection ➔ Show List ➔ Masters ➔ Bank Details
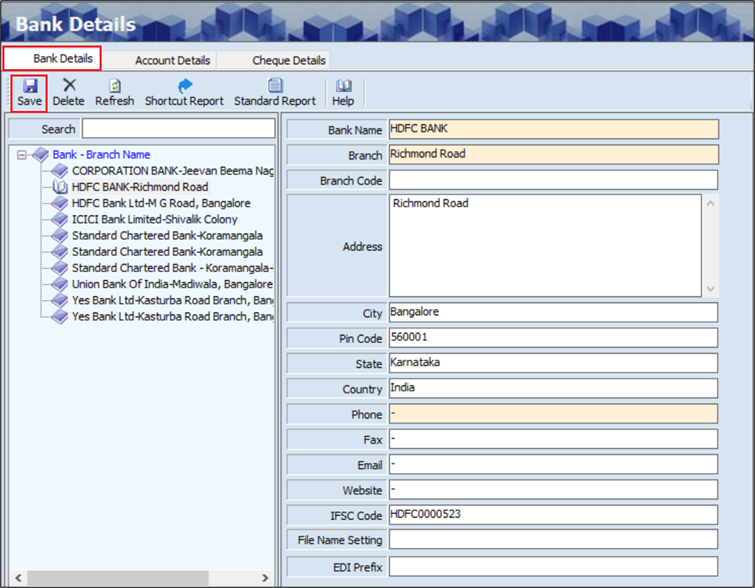
- The user can search or view the existing bank details based on the Bank and Branch Name.
- The Bank Details screen allows the user to enter the details in three tabs as mentioned below.
- Bank Details
- Account Details
- Cheque Details
- The Bank Details section allows the user to enter details such as the Bank Name, Branch, Phone Number and IFSC Code.
- The user can enter details such as the Branch Code, Address, City, Pin Code, State, Country, Fax, Email, Website, File Name Setting and EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) Prefix.
- Click Save, the following message will appear.
- Click Yes, the Bank and Branch Name will appear in the left panel of the screen.
¶ Delete Bank Details
The Delete option allows the user to delete the existing or added bank details.
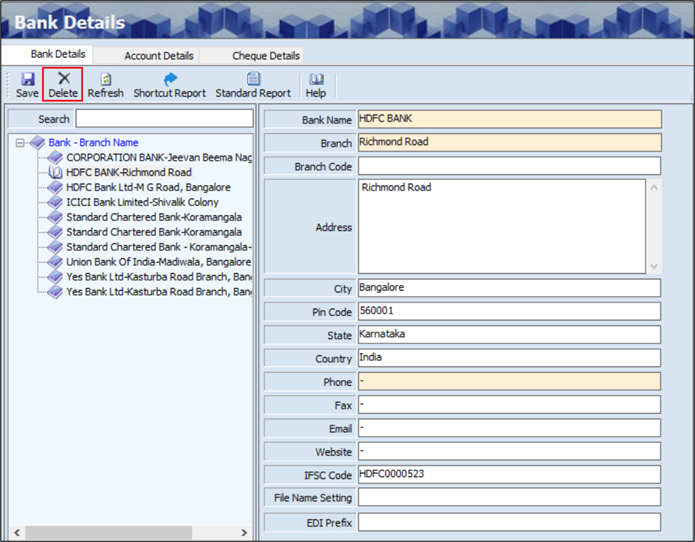
- The user must select the Bank and Branch Name from the left panel of the screen.
- Click Delete, the following screen will appear.
- Click Yes, to delete the bank details.
¶ Add Account Details
The Account Details screen allows the user to add the details of the bank account for the particular bank.
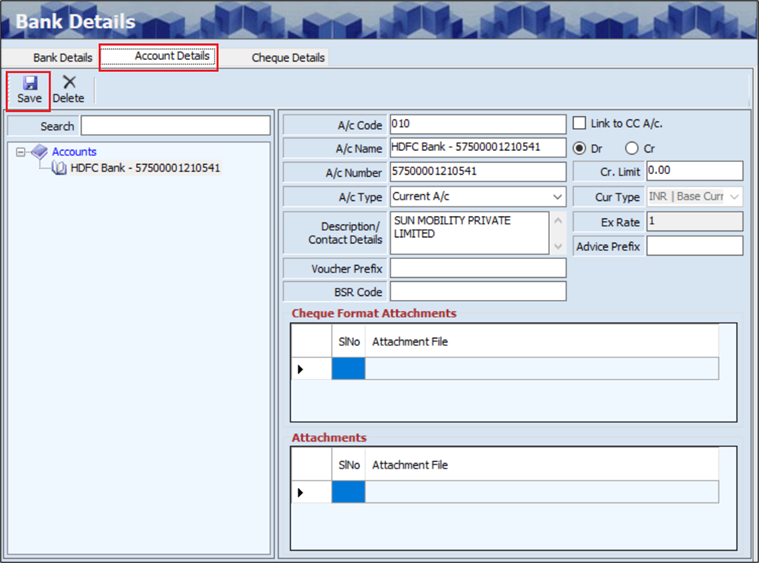
- The user can search or view the existing account details based on the Account Name.
- The user must enter details such as the A/c Code, A/c Name and A/c Number.
- The user must select the A/c Type and Currency Type from the dropdown list.
- Once the user selects Currency Type, the Exchange Rate will appear automatically.
- The user can enter details such as the Description / Contact Details, Voucher prefix, BSR Code, Credit Limit and Advice Prefix.
- The user can upload Cheque Format Attachments, if required.
- The user can upload Attachments, if required.
- Click Save, the following message will appear.
- Click Yes, the Account Name will appear in the left panel of the screen.
¶ Delete Bank Account
The Delete option allows the user to delete the existing or added bank account.
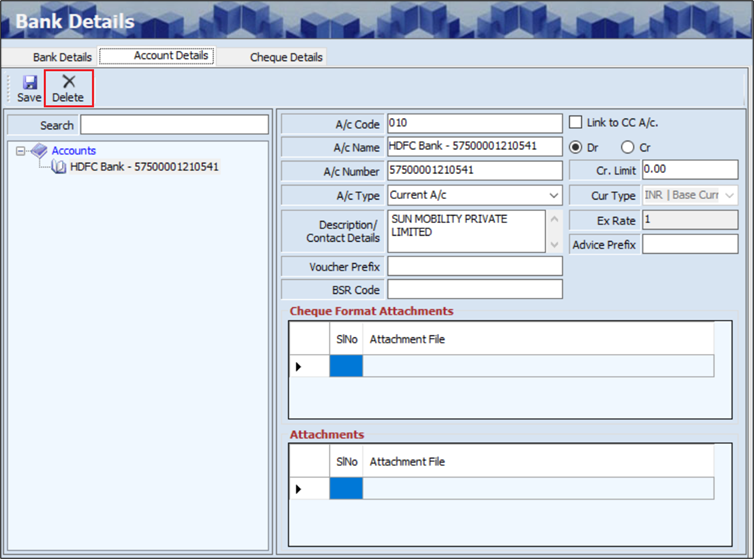
- The user must select the Account Name from the from the left panel of the screen.
- Click Delete, the following screen will appear.
- Click Yes, to delete the account.
¶ Add Cheque Details
The Cheque Details screen allows the user to add the details of the cheque for the particular bank and account.
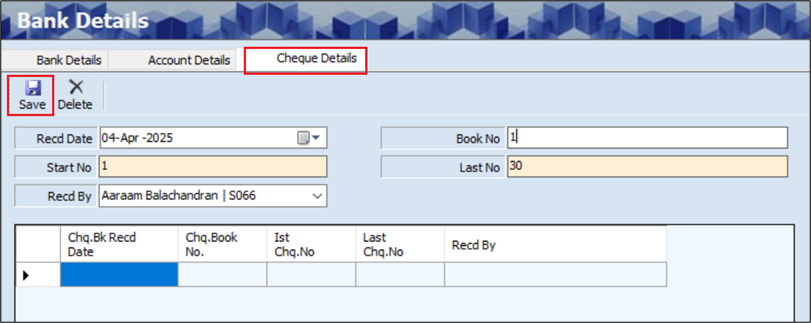
- The Cheque Details screen displays the Received Date.
- The user can edit the Received Date, if required.
- The user must enter the Start Number.
- The user must enter the Last Number.
- The user must select the Received By from the dropdown list.
- The user can enter the Book Number, if required.
- Click Save, the following screen will appear.
- Click Yes, added cheque details will appear as shown below.
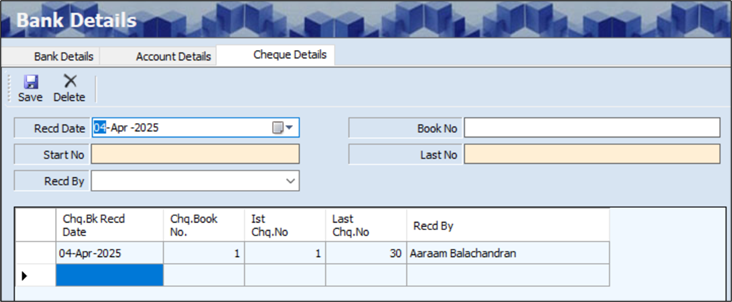
- The Cheque Details section displays details such as the Cheque Bank Received Date, Cheque Book Number, 1st Cheque Number, Last Cheque Number and Received By.
¶ Delete Cheque Details
The Delete option allows the user to delete the existing or added cheque details.
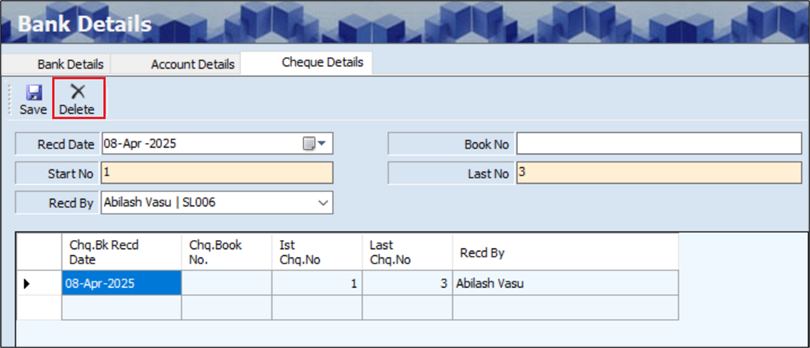
- The user must select the grid to select the row.
- Click Delete, the following screen will appear.
- Click Yes, to delete the cheque details.
¶ Functional Use Cases
| Sl. No. | Use Case | Business Scenario | Functional Outcome in ERP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Add company bank accounts | The company opens a new bank account for business transactions. | The user adds bank account details such as account number, IFSC code, and branch in the ERP. |
| 2 | Maintain multiple bank accounts | The company operates with multiple banks (e.g., SBI, HDFC, ICICI). | The ERP stores and manages all bank account records separately under Bank Details. |
| 3 | Link bank accounts to transactions | Payments and receipts are made through specific bank accounts. | The ERP allows linking of the appropriate bank account while processing receipts or payments. |
| 4 | Set a default bank account | Most payments are made from a primary bank account. | The ERP uses the default bank account automatically unless manually changed. |
| 5 | Edit bank account details | The bank changes the branch IFSC code or contact details. | The user updates bank information in the system, ensuring transactions remain accurate. |
| 6 | Display bank details for reference | The user needs to confirm the bank account information during a transaction. | The ERP displays the full bank details for verification on relevant screens. |
| 7 | Enable bank-wise reporting | Management wants to track transactions based on each bank account. | The ERP generates bank-wise reports for payments, receipts, and balances. |
| 8 | Control access to bank account data | Only authorized personnel should manage or view sensitive bank information. | The ERP applies role-based access control to protect bank account data. |
| 9 | Sync bank details with financial transactions | Transactions like Payments, Receipts, and Bank Reconciliation rely on accurate bank data. | The ERP ensures consistency by using bank details across all finance modules. |
¶ Use Case Scenario
- Click here for a detailed use case scenario for the Bank Details transaction.
¶ Transaction Checklist
| Steps | Checklist Item | Details / Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Collect bank account information | Ensure all required data such as bank name, account number, IFSC code, and branch are available |
| Identify type and purpose of the account | Decide if the account is used for payments, receipts, payroll, etc. | |
| Assign user roles for access | Determine which users can create, view, or edit bank details | |
| 2. Bank Setup | Enter bank account in the ERP | Add details such as account name, number, bank, IFSC, and branch |
| Mark account as default (if required) | Define the primary account to be used for transactions | |
| Assign active status | Ensure the account is set to active for use in transactions | |
| 3. Validation | Verify account number and IFSC | Check accuracy of bank details to prevent failed transactions |
| Review for duplicates | Ensure the same account is not created multiple times | |
| Confirm linkage with financial modules | Validate that bank account appears in payment, receipt, and reconciliation screens | |
| 4. Maintenance | Edit account details when changes occur | Update IFSC code or branch name as per bank notifications |
| Deactivate closed or unused accounts | Prevent future use while retaining historical data | |
| Highlight inactive accounts visually | Display inactive accounts in red for identification | |
| 5. Reporting & Access | Test bank-wise reporting | Generate reports to verify bank usage and balances |
| Restrict access to sensitive bank information | Apply role-based permissions to limit editing/viewing rights | |
| Ensure the audit trail is maintained | Track user activity related to creation or modification of bank records |